11 Revealing Classroom vs Digital Learning Statistics for 2025
We earn a commission from partner links on this site. This doesn’t affect our opinions or evaluations.
As online learning continues to expand, increasing numbers of individuals have begun to view it as a dependable alternative to traditional classroom education. The COVID-19 pandemic has intensified this movement, and it’s evident that the global education landscape is experiencing remarkable transformations.
What exactly is the extent of these shifts? Could digital learning effectively replace face-to-face instruction? And should we wholeheartedly adopt this approach?
These are precisely the questions we’ve endeavored to explore through the comprehensive in-person vs online learning statistics compiled in this article.
Below, we’ve distilled 11 of the most current trends, attitudes, and engagement metrics comparing these two educational approaches.
Are you prepared? Let’s begin our exploration.
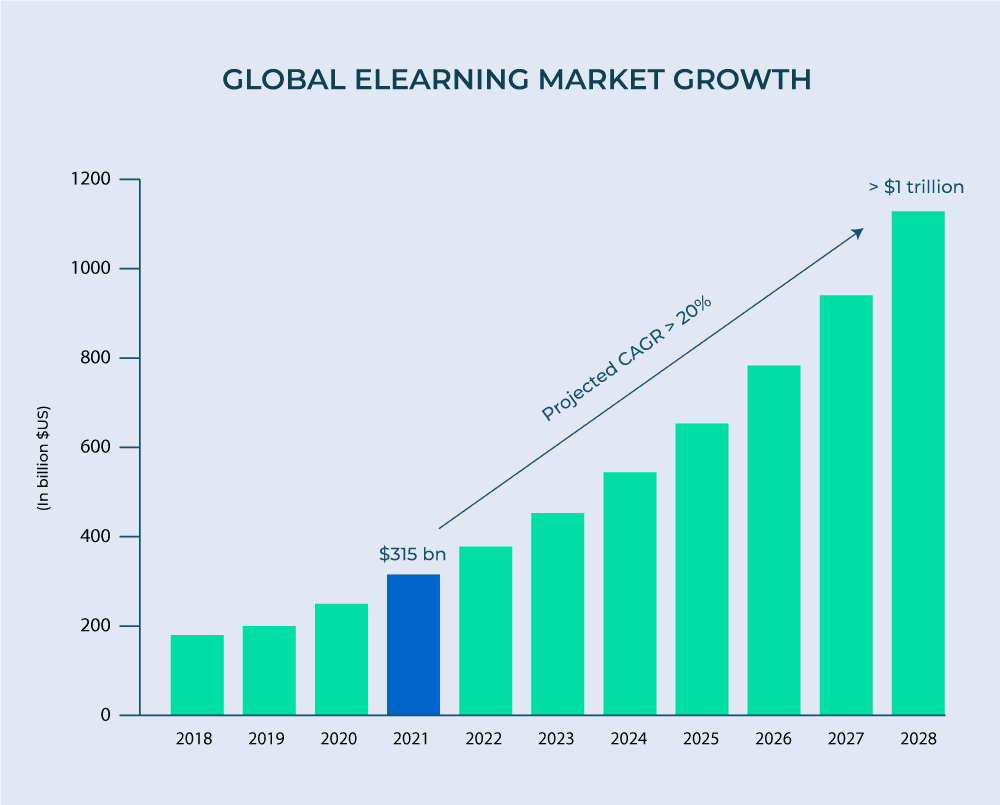
Projected global online learning market growth, 2018 – 2028
Despite eLearning currently representing just a fraction of the broader education and training landscape, these figures clearly indicate that long-term momentum strongly favors digital learning compared to traditional in-person instruction.
Furthermore, this progression may potentially accelerate even faster with expanding internet accessibility and the emergence of groundbreaking tools, platforms, and services supporting this educational segment.
While the online learning sector demonstrates impressive growth, it continues to constitute a relatively modest portion of the overall education industry.
Across all educational levels, projections indicate the global education market will reach $10 trillion in revenue by 2030. Although eLearning will undoubtedly play an increasingly significant role in this expansion going forward, it will still comprise slightly more than 10% of the total market value.
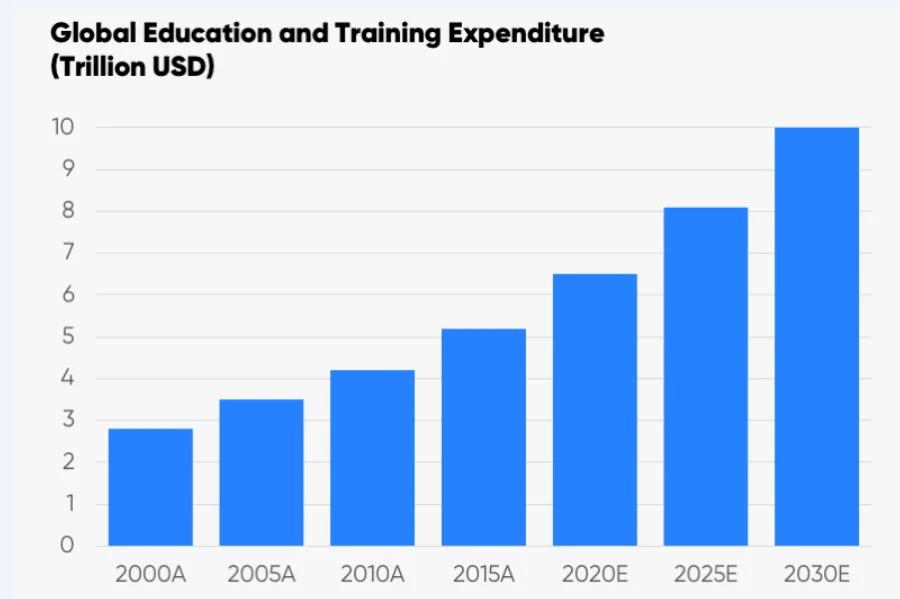
Projected education market growth (Source: HolonIQ)
Despite its remarkable expansion rate, digital learning continues to trail behind traditional in-person education regarding absolute value contribution. This dynamic will likely persist for the foreseeable future, varying based on how these two educational approaches integrate and complement each other.
Throughout recent years, online degrees and educational programs have steadily gained mainstream acceptance, beginning with blended learning approaches.
According to the most recent research, 75% of undergraduate students in the United States have participated in at least one distance learning course, with 44% of these students enrolled predominantly in distance learning programs.
The total number of undergraduates taking at least one online course increased dramatically from 6 million in 2019 to 12 million by autumn 2020. This represents a year-over-year increase of 97%, primarily driven by the sudden implementation of stay-at-home mandates during the pandemic.
Many aspects of these trends are anticipated to continue, given the clear advantages online learning offers to students, educators, and educational institutions alike.
Students aren’t merely enrolling in online courses—they’re genuinely appreciating the experience.
Among the approximately 1.4 billion students affected by the sudden closure of schools, colleges, and various learning institutions, 78% express satisfaction with their online learning experiences.
Notably, 41% of these students consider online learning superior to traditional classroom settings, while 38% perceive it as comparable in quality.
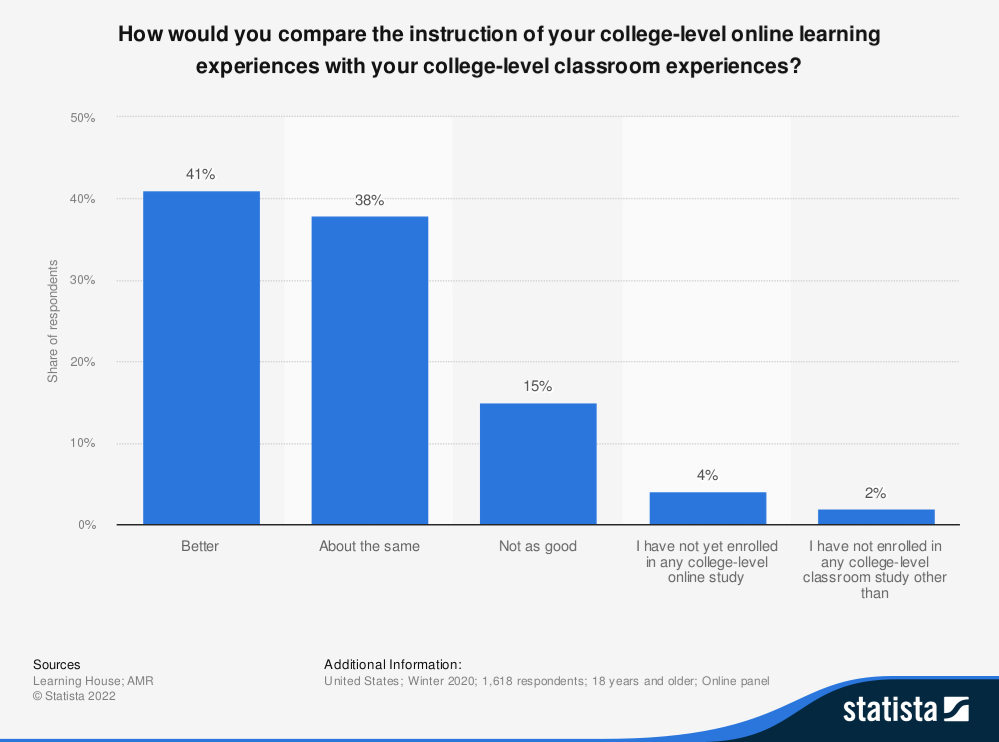
Several factors contribute to this preference, including:
Academic institutions and teaching professionals are increasingly embracing this shift as well.
When evaluating content delivery methods, instructor-student interactions, and long-term educational outcomes, 77% of educators assert that online learning now equals—or even surpasses—conventional educational approaches.
The significance of this trend becomes even more pronounced considering that higher education establishments and their faculty have historically demonstrated a preference for face-to-face instructional methods.
Consequently, it appears that the effectiveness of digital learning environments is gradually transforming the perspectives and institutional biases within traditional educational systems.
Thanks to substantial efficiency improvements and significantly lower operational expenses associated with online degree programs, students can realize savings exceeding $36,000 compared to traditional in-person degrees.
This calculation encompasses the comprehensive costs (including tuition, attendance-related expenses, etc.) for public higher education institutions over a four-year period.
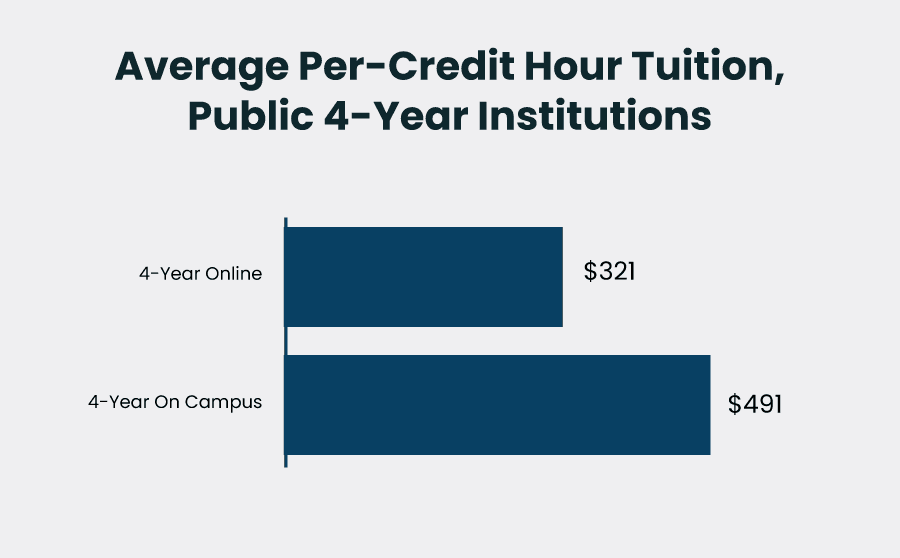
The per-credit-hour cost of an online vs on-campus public university degree.
Interestingly, the disparity in actual tuition expenses isn’t quite as dramatic. An online degree from a public university averages approximately $38,496 compared to $37,500 for its in-person equivalent.
As the combined forces of technological advancement, economies of scale, and market competition intensify, we may be witnessing the beginning of the end for inflated higher education costs worldwide.
With increasing acceptance of digital learning approaches, we could soon experience fundamental disruption throughout the higher education landscape.
Beyond simply offering downloadable resources, reusable video content, and other digital assets, online education can reach substantially broader audiences without the constraints of physical classroom capacity or infrastructure limitations. This scalability creates opportunities for significantly reducing costs with each additional enrolled student.
Enhancing student knowledge retention has consistently remained a fundamental concern throughout educational history.
Exceptional educators continuously develop innovative methodologies to capture attention, maintain engagement, and cement knowledge within students’ understanding, yet digital learning environments potentially unlock an entirely new spectrum of possibilities.
Research shows that the ability to engage with course material at an individualized pace and revisit instructional content multiple times has elevated student knowledge retention rates from 25% to an impressive 60%.
This percentage can increase substantially when incorporating enhanced visual elements, personalized learning paths, and flexible scheduling options.
Digital learning environments demonstrably reduce required employee hours by approximately 40% to 60% compared to traditional classroom instruction, representing another dimension of the efficiency improvements mentioned previously.
Furthermore, eliminating the need for physical classrooms and supporting infrastructure naturally generates additional labor hour savings.
These cumulative efficiencies could ultimately translate into cost reductions for students, contributing to a progressively more affordable higher education and vocational training ecosystem.
Among the most compelling online versus face-to-face learning statistics are those highlighting environmental advantages.
Studies indicate that online learning environments consume approximately 87% less energy than traditional classroom settings and generate 85% lower carbon dioxide emissions.
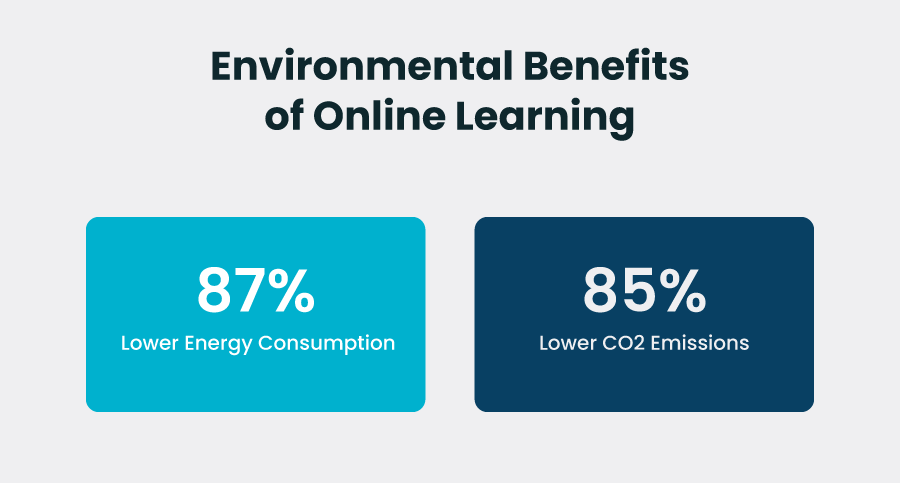
In our current era where energy efficiency represents a global priority, this particular advantage carries exceptional significance.
Additionally, as climate action continues gaining mainstream attention and support, digital learning environments will likely be increasingly proposed as an integral component of broader sustainability solutions.
Despite the numerous advantages online learning offers to educators, students, and academic institutions, one crucial stakeholder group remains to be fully convinced—parents.
While most families acknowledge the cost-effectiveness, reduced commuting requirements, and enhanced retention rates that digital education provides, they continue to value the importance of experiencing an “Authentic College Environment.”
The capacity of traditional education to foster social and emotional development has prompted many families to maintain their preference for in-person learning experiences, with parents generally not viewing online education as a complete substitute for conventional classroom settings moving forward.
Recent survey data reveals that merely 16% of families express preference for exclusively online learning models, while 39% endorse blended learning approaches. By comparison, an equal 39% of families strongly support entirely in-person educational programs.
Despite increasing adoption rates, several significant challenges associated with online learning have emerged that must be addressed before digital-only college degrees and K-12 education can become widely accepted as standard practice.
Beyond the reduced opportunities for student social interaction, numerous additional concerns require attention, including focus and attention management issues and difficulties facilitating effective student collaboration in virtual environments.
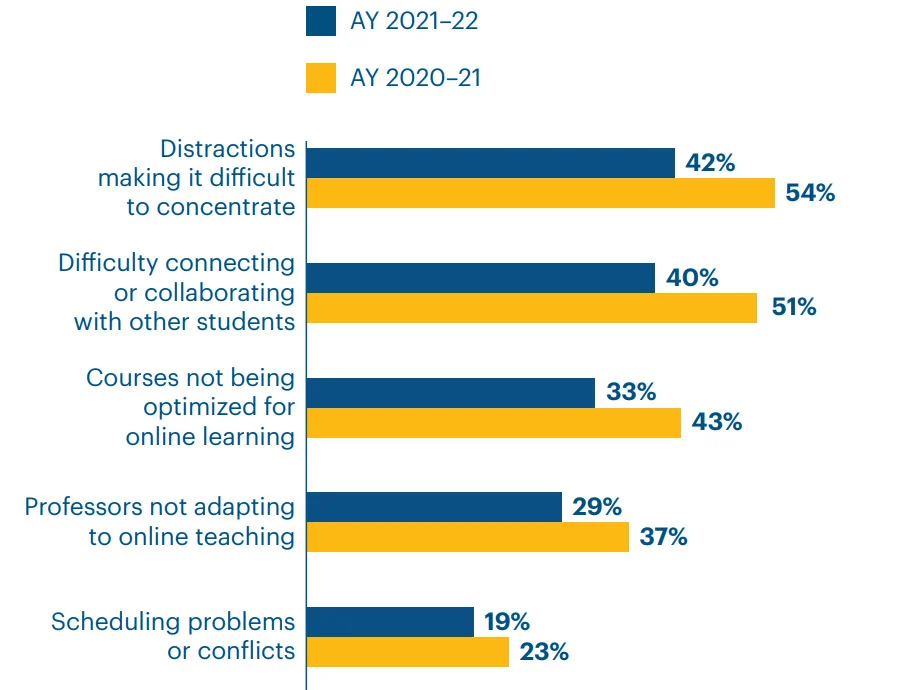
Many of these challenges are currently being addressed through various online community platforms that facilitate meaningful discussions and networking opportunities among learners. Alternative platforms incorporate sophisticated audience engagement tracking systems to monitor and notify instructors about student attentiveness issues and potential distractions.
This completes our comprehensive analysis of the essential in-person vs online learning statistics you should understand in 2025.
We currently find ourselves in a transformative period for digital education, with numerous innovative technologies emerging at the forefront of this evolution.
Nevertheless, with substantial growth inevitably come significant adjustment challenges. Within the digital learning ecosystem, these challenges correspond to the key obstacles we’ve highlighted above.
Therefore, for the foreseeable future, traditional in-person learning will maintain its relevance. Rather than complete replacement, we’re more likely to witness the development of sophisticated blended learning models where reliance on physical classroom environments gradually diminishes over time.
Both modes have their share of advantages and drawbacks. While online learning allows for self-paced learning, revisiting lessons, and more, it lacks the level of engagement and focus often seen with in-person learning.
Online education is fundamentally less expensive compared to in-person classes, and consumes far fewer resources in terms of infrastructure and labor. Apart from substantial savings on transportation expenses, student housing, and more, it also caters to a much wider audience, creating the potential to bring down expenses per student.
Besides being ineffective for specific subjects and classes requiring applied learning, online learning can lack the social component, depriving the students of the experiences we tend to associate with learning.
Besides being ineffective for specific subjects and classes requiring applied learning, online learning can lack the social component, depriving the students of the experiences we tend to associate with learning.

Daniel NicFounder, SellingOnliceCoursesGuide.comis an entrepreneur and digital education specialist who founded sellingonlinecoursesguide.com, a platform dedicated to helping creators and educators successfully navigate the online course marketplace. Through his website, he shares insights and strategies for developing, marketing, and monetizing online educational content. His work focuses on empowering course creators to build sustainable online businesses while effectively sharing their knowledge with students worldwide.

Daniel Nic is an entrepreneur and digital education specialist who founded sellingonlinecoursesguide.com, a platform dedicated to helping creators and educators successfully navigate the online course marketplace. Through his website, he shares insights and strategies for developing, marketing, and monetizing online educational content. His work focuses on empowering course creators to build sustainable online businesses while effectively sharing their knowledge with students worldwide.

We respect your privacy and will never spam you.